Evolution of LTE 4G Network & Its Techniques
WHAT IS 4G ?
 |
4G Network Architecture |
4G is the fourth generation of mobile
phone mobile communication technology standards.
It is a successor to the third
generation (3G) standards.A 4G system provides mobile “ Ultra Broadband speed” – to be counted in
gigabytes per second.In March 2008, the International Telecommunications Union-Radio communications sector (ITU-R) specified a set of requirements for 4G standards, named the IMT-Advanced.
Set peak speed requirements for 4G service at 100 Mbit/s for high mobility communication and 1 Gbit/s for low mobility communication.
The peak bit rate is further improved by smart antenna arrays for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) communications.
A 4G system does not support traditional circuit switched telephony service, but all-Internet Protocol (IP) based communication such as IP telephony.
 |
Evolution of 4G Network |
EVOLUTION OF 4G
In April 2006, KT started the
world's first commercial mobile WiMAX service in Seoul, South Korea.
In February 2007, the Japanese
company NTT DoCoMo tested a 4G communication system prototype with 4×4 MIMO at
100 Mbit/s while moving, and 1 Gbit/s while stationary.
In Dec 2009, The first commercial LTE
deployment was by TeliaSonera & NetCom. The modem devices on offer
were manufactured by Samsung, and the network infrastructure created
by Huawei & Ericsson.
 |
3G Vs 4G |
SYSTEM KEY COMPONENTS OF 4G
a) System standards
·
LTE Advanced
·
WiMAX 2
b)
Multiplexing and access schemes
·
OFDM+ MIMO, W–OFDM, MC-CDMA
·
IPv6 SUPPORT
d)
Advanced antenna systems
·
Multiple antenna technologies are
used to achieve high rate, high reliability and long communication range.
e)
Software-defined radio (SDR)
·
Standards constituted by a 4G
device can be realized using SDR.
A) System standards
LTE
1) Long Term Evolution (LTE) is a radio
platform technology that will allow operators to achieve even higher peak
throughputs than HSPA+ in higher spectrum bandwidth.
2) LTE uses Orthogonal Frequency Division
Multiple Access (OFDMA)
on the downlink, which is well suited to achieve high peak data rates in high
spectrum bandwidth.
LTE capabilities include:
1) Downlink peak data rates up to 326 Mbps
with 20 MHz bandwidth
2) Uplink peak data rates up to 86.4 Mbps
with 20 MHz bandwidth
3) Operation in both TDD and FDD modes
4) Scalable bandwidth up to 20 MHz,
covering 1.4 MHz, 3 MHz, 5 MHz, 10 MHz, 15 MHz, and 20 MHz in the study phase
5) Reduced latency, up to 10 milliseconds
(ms) round-trip times between user equipment and the base station, and to less
than 100 ms transition times from inactive to active
WiMAX 2
·
WiMAX stands for Worldwide
Interoperability for Microwave Access. WiMAX 2 also called Wireless
MAN-Advanced has become the first true 4G technology to be approved by the IEEE
and ITU.
·
This technology supports MIMO,
femto cells, self-organizing networks & relays, and multicarrier operation.
It supports both 120Mbps downlink and 60Mbps uplink speeds.
·
The unique and excellent
infrastructure of WiMAX is offering Ultra-Wideband and providing range from 2 to
10 GHz and outstanding time response.
 |
Shows Mobility & Coverage v/s Data Rates of different Technologies |
b) Multiplexing and access schemes in 4G
OFDM
·
Orthogonal frequency-division
multiplexing (OFDM) is a frequency division multiplexing (FDM) scheme that uses
a digital multi-carrier modulation method.
·
OFDM uses the spectrum more
efficiently by making all the sub-carriers orthogonal to one another, using
fast Fourier transform (FFT) to prevent interference between the closely spaced
sub-carriers.
·
In OFDM, the guard band is
reduced by the orthogonal packing of the subcarriers, improving the spectral
efficiency .
·
Since each carrier in an OFDM
signal has a very narrow bandwidth (i.e. few kHz), the resulting symbol rate is
low.
·
Due to the orthogonal nature of
the modulation, these multiple sub-carriers overlap in the frequency domain,
but do not cause Inter-Carrier Interference (ICI).
·
In OFDM, the guard band is
reduced by the orthogonal packing of the subcarriers, improving the spectral
efficiency.
 |
FFT- FAST FOURIER TRANSFORM |
 |
OFDM MODEL |
SYSTEM KEY COMPONENTS OF 4G
IPv6 SUPPORT
The IP address is based on IPv6
Ø IPv4 X.X.X.X (32 bits)
Example: 216.37.129.9
Ø IPv6 X.X.X.X.X.X (128 bits)
 |
IPV6 SUPPORT EXAMPLE |
·
Needs for security and
manageability
·
4G system uses the Internet
Protocol version 6 (IPv6) to locate devices.
·
There is room for approximately
3.40 * 1038 unique
addresses.
·
There are enough addresses for
every phone to have a unique address.
·
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
is a methodology and group of technologies for the delivery of voice
communications and multimedia sessions over Internet
Protocol (IP) networks
 |
IP BASED CORE NETWORK |
c) Advanced antenna systems
Smart antennas (MIMO)
are antenna arrays with smart
signal processing algorithms used to identify spatial signal signature such as
the direction of arrival (DOA) of the signal, and use it to
calculate beam forming vectors, to track and locate the antenna beam
on the mobile/target.
 |
Transmitter with multiple antennas |
 |
Smart antennas Types |
·
It offers significant increases
in data throughput and link range without additional bandwidth or increased
transmit power.
·
It achieves this goal by
spreading the same total transmit power over the antennas to achieve
an array gain that improves the spectral efficiency and to achieve a diversity gain that
improves the link reliability.
Example of advanced antenna:
d) Software-defined radio (SDR)
·
Due to the constant evolution of
mobile communication systems (2G, 3G, and 4G), the wireless industry is facing
problems in global roaming to provide different services to the mobile
subscribers. SDR technology promises to solve these problems by implementing
the radio functionality as software modules running on a generic hardware
platform.
·
The main purpose of SDR is to
make a user terminal operate in different kinds of wireless networks,
overcoming power, cost, size, and compatibility limitations.
·
Flexibility and reconfigurability
·
Interoperability
·
Connectivity
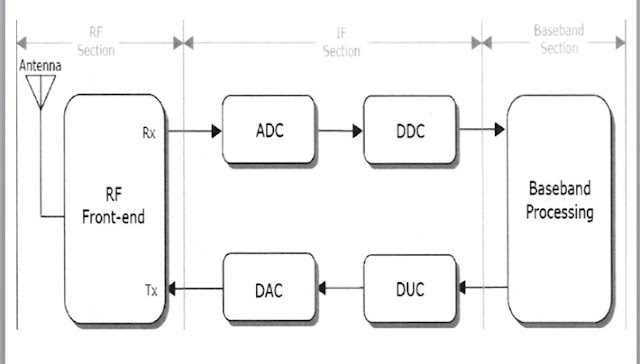 |
Block Diagram of a Generic Software Defined Radio |



troscomMalwo1978 Katie Harris Download
ReplyDeleteneckpakligfharg
0riberVdiuge Mary Ortiz click here
ReplyDeletemehrparneso
osolVfoere Kristy Brooks Link
ReplyDeleteFonePaw
Sketchbook PRO
Movavi Video Converter
lentlocalons
Very useful post and thanks for sharing!!
ReplyDeleteSensormatic
Phone Holder
Anti Theft Tablet Security Stand